Installing MikroTik CHR on a Virtual Server

MikroTik Cloud Hosted Router (CHR) is a specialized version of RouterOS that's optimized for virtual machine environments, functioning as a complete operating system.
In this guide, we'll walk you through the process of installing and configuring MikroTik CHR on your virtual server.
System Requirements
You can install MikroTik CHR on any of our virtual server plans, including the entry-level configuration with:
- 1 CPU core
- 1 GB RAM
- 10 GB NVMe storage
This guide demonstrates the manual installation process using a i9-PROMO-1 virtual server.
Prerequisites
- Order a virtual server through your control panel or use an existing server
- For this example, we'll use:
- Plan: i9-PROMO-1
- Base OS: Ubuntu 24.04 (required for CHR deployment)
Installation Steps
1. Server Setup
- Your server will be ready within 2 minutes after ordering
- Connect to the server using SSH credentials provided in your activation or OS reinstallation email
- For SSH connection guidance, refer to our How to connect to the server (Linux) guide
2. Downloading CHR Image
- Visit the official MikroTik download page
- Download the Raw disk image version of CHR (we'll use version 7.18.2 in this example)
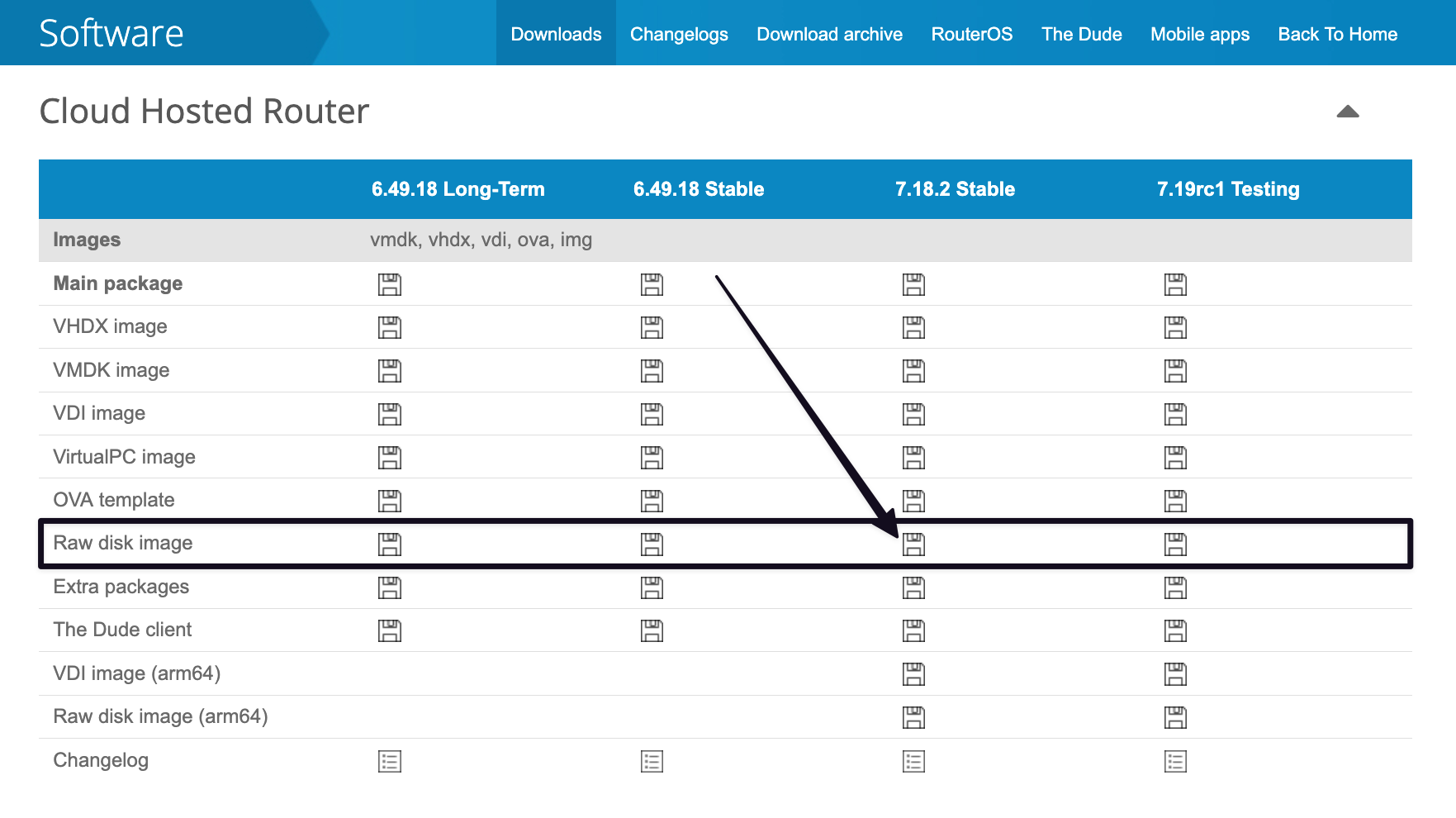
- Right-click the download icon and copy the download link (e.g., https://download.mikrotik.com/routeros/7.18.2/chr-7.18.2.img.zip)
- Download the image to your virtual server:
cd /tmp
wget <LINK> -O chr.img.zipFor example:
cd /tmp
wget https://download.mikrotik.com/routeros/7.18.2/chr-7.18.2.img.zip -O chr.img.zip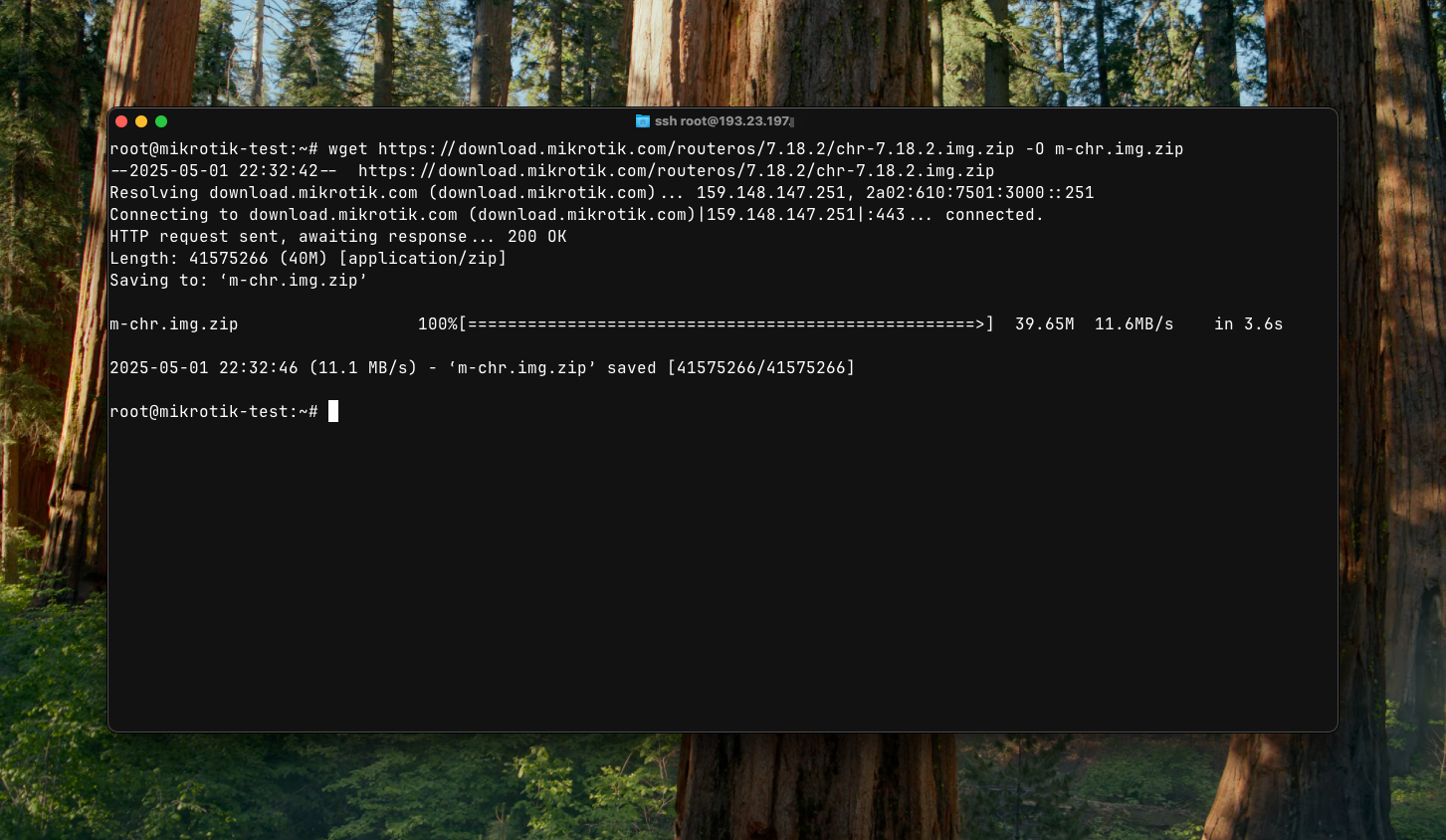
3. Image Deployment
WARNING
This process will delete all data from your server. Make sure to back up any important data before proceeding!
Install gunzip:
apt -y install gunzipExtract the downloaded image:
gunzip -c chr.img.zip > chr.imgSwitch the disk system to read-only mode:
echo u > /proc/sysrq-triggerWrite the image to the virtual disk:
dd if=chr.img of=/dev/vda bs=4M oflag=syncReboot the server to initialize CHR:
echo 1 > /proc/sys/kernel/sysrq
echo b > /proc/sysrq-triggerAfter executing the last command and pressing [Enter], your SSH connection may appear to hang - this is expected behavior.
You can safely disconnect from your virtual server at this point. The remaining setup will be performed through the web VNC interface.
4. Network Configuration
Now we need to access the VM control panel to connect to our server via VNC.
Accessing the System
- Log into our VM control panel
- Select the server where you installed MikroTik CHR
- Connect to the server through the VNC console
- Default credentials:
- Username: admin
- Password: (leave empty)
System Setup
- Skip the software license agreement (press 'n')
- Set a new administrator password (minimum 8 characters recommended)
- Configure network settings using parameters from your control panel:
/ip address add address=<IPv4>/32 network=<Gateway> broadcast=<IPv4> interface=ether1
/ip route add dst-address=0.0.0.0/0 gateway=<Gateway>
/ip dns set servers=1.1.1.1,1.0.0.1Where:
<IPv4>is your server's IP address<Gateway>is typically172.16.0.1(for RZ9, EP lineups) or10.0.0.1(for the i9-PROMO lineup)
You can verify your server's internet connectivity by running:
ping 1.1.1.1If configured correctly, you should see replies from Cloudflare's DNS (1.1.1.1): 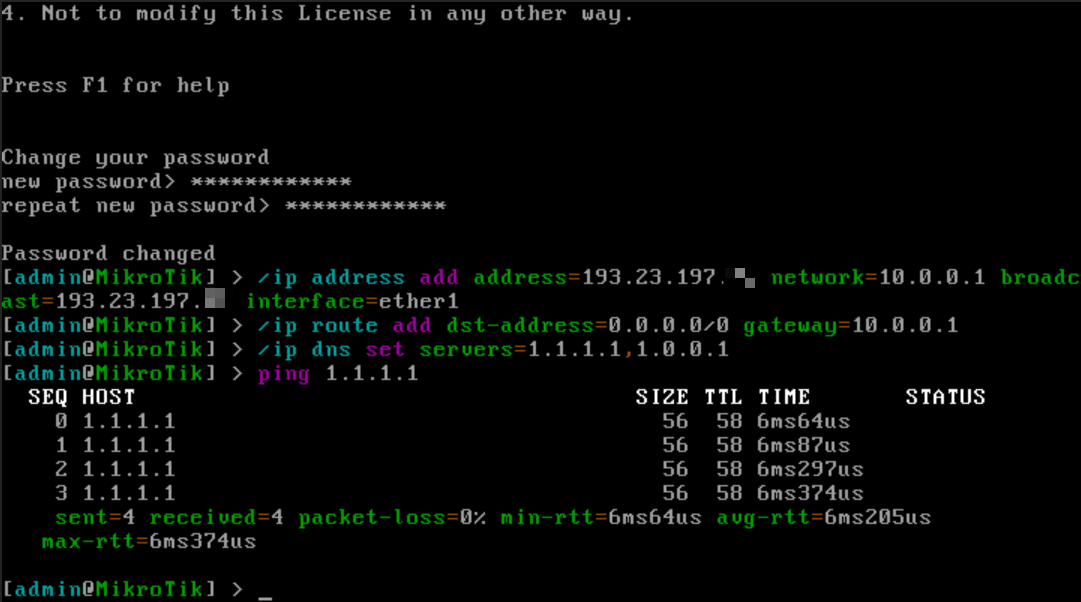
Your MikroTik CHR is now ready for further configuration and use. You can now connect via SSH as well.
Additional Configuration
Creating a New User
For enhanced security, we recommend creating a new user and removing the default admin user.
Create a new user by running:
user/add name=usernameWhere username is your desired login name.
The system will prompt you to:
- Assign a group - type
full - Set a password - use at least 8 unique characters
Removing the Admin User
After creating your new user:
- Log out of the current session:
/quit- Log in with your new credentials via SSH or VNC
- Remove the admin user:
user/remove adminSecuring Services
By default, MikroTik runs several services on various ports, including:
- Telnet
- FTP
- HTTP server
- SSH
- API
- Winbox
- SSL API
These services may expose your server to security risks, as malicious bots often attempt to brute-force routers on the internet.
To check currently running services:
ip/service/print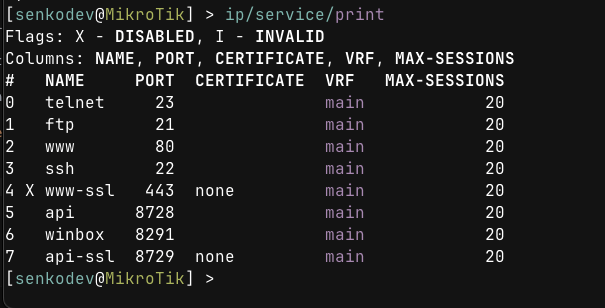
Disable unused services:
ip/service/disable n,n,n,nWhere n represents the service number to disable.
Examples:
ip/service/disable 0,1,2,5,7 # Disables Telnet, FTP, HTTP, API, and SSL API
ip/service/disable 3 # Disables SSH only
ip/service/disable 5,7 # Disables API and SSL API only
ip/service/disable 1 # Disables FTP onlyChanging SSH Port
For additional security, change your SSH port to a non-standard number (e.g., 59871):
set 3 port=PORTWhere PORT is your preferred port number.
Example:
set 3 port=59871License Information
Check your MikroTik CHR license status:
/system/license/printCHR offers four license levels:
- free: 1 Mbps speed (default)
- p1 (perpetual-1): $45, 1 Gbit speed
- p10 (perpetual-10): $95, 10 Gbit speed
- p-unlimited (perpetual-unlimited): $250, Unlimited speed
The default free license allows indefinite use but limits throughput to 1 Mbps per interface.
For more information about licensing, visit the official MikroTik documentation.